The devices are aimed at high speed serial busses including PCIe 5.0/4.0, CXL 2.0/1.0, USB4 Version 2.0, Gen3/Gen2, USB 3.2 Gen 2/Gen 1, Thunderbolt 4, DisplayPort 2.0/1.4 and SAS 3.0.
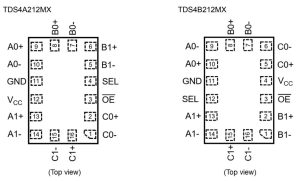
Made on the company’s ‘TaRFSOI’ silicon-on-insulator CMOS process, both parts have the same switch, and same 2.4 x 1.6 x 0.4mm XQFN16 package, but pinouts are different (right) to optimise the parts for different applications.
TDS4A212MX’s is optimised for easy board layout, its differential specs are:
-3dB Bandwidth 26.2GHz
Insertion loss -1.1dB (10GHz), -1.9dB (16GHz)
Return loss -17dB (10GHz), -18dB (16GHz)
Off isolation -17dB (10GHz), -11dB (16GHz)
Crosstalk -32dB (10GHz), -30dB (16GHz)
TDS4B212MX is optimised for high frequency performance, its differential specs are:
-3dB Bandwidth 27.5GHz
Insertion loss -0.9dB (10GHz), -1.4dB (16GHz)
Return loss -20dB (10GHz), -16dB (16GHz)
Off isolation -16dB (10GHz), -14dB (16GHz)
Crosstalk -44dB (10GHz), -36dB (16GHz)
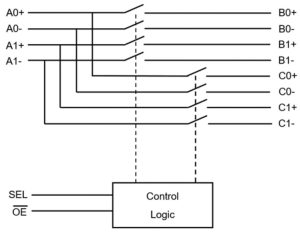 When switching, port A is connected to either port B or port C, controlled by the SEL input, and all switches are high-impedance if OE is held high regardless of SEL, dropping consumption to 10μA max.
When switching, port A is connected to either port B or port C, controlled by the SEL input, and all switches are high-impedance if OE is held high regardless of SEL, dropping consumption to 10μA max.
Operation is over -40 to 85°C and 1.6 to 3.6V, and enabled consumption is typically 60μA (150μA max).
Signals can vary across 0 to 2V common-mode and up to 1.8V differentially.
Propagation delay of the faster (…B…) part is typically 30ps, bit-to-bit skew is 4ps and channel to channel skew is 2ps.
It takes a maximum of 100μs from power-up or output-enable for the outputs to be valid, and SEL turns a port ‘on’ in a maximum of 180ns, and ‘off’ in 18ns max. Output disable takes 21ns max.
Use is expected expanding peripheral devices in PCs, in servers and in mobile devices.
Web pages
