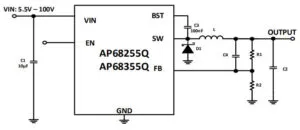
The parts are similar, but rated at 5 to 100V or 5 to 80Vin, and 2.5A or 3.5A out.
There are not synchronous rectifier ICs. Instead they include a 500mΩ (950mΩ max) series switch and expect a high current Schottky diode to be connected externally.
Part numbers are AP68255Q (8V 2.5A), AP68355Q (80V 3.5A), AP6A255Q (100V 2.5A or AP6A355Q (100V 3.5A).
Control is through a constant on-time scheme, with the series switch turned on every time the output drops below its regulation threshold.
“This technique results in fast load/line transient response, easy loop stabilisation, and low output voltage ripple, making the devices easier to incorporate by requiring fewer external components,” claimed Diodes. “On-pulse timing is calculated, inversely proportional to input voltage and directly proportional to output voltage, to maintain a pseudo-fixed frequency over the input voltage range” – at ~300kHz. Minimum off-time is typically 200ns.”
Constant frequency operation eases EMI filtering as does, it claims, the company’s proprietary gate-driver which is intended to “reduce switch node ringing effects without sacrificing the turn-on and turn-off times of the n-channel mosfet switch”.
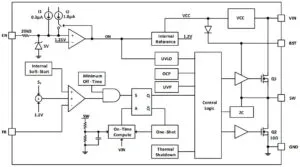 Although this is an asynchronous buck, there is an internal 10Ω mosfet in the synchronous rectifier position (labelled Q2 in diagram left).
Although this is an asynchronous buck, there is an internal 10Ω mosfet in the synchronous rectifier position (labelled Q2 in diagram left).
What is that for?
“Q2 is a small low-side FET to help refresh the bootstrap capacitor voltage in the event of long period no switching,” the company told Electronics Weekly. “This usually will happen in PFM [pulse-frequency modulation] and no load situations.”
Other features include an enable pin which can shut the device down to 5.6μA as well as programme the under-voltage lock0out threshold if two resistors are connected to it.
Over-current protection has frequency fold-back to reduce junction temperature during faults, and is backed by over-temperature protection with hysteresis between 160 and 140°C. Nominal operating range is -40 to +125°C.
Qualification is to AEC-Q100 Grade 1, manufacturinng facilities are IATF 16949 certified and there are supporting PPAP documents.
For non-automotive use there are related industrial-grade parts.
As an example, find the 100V 3.5A AP6A355Q on this Diodes web page.