S. Himmelstein | June 13, 2023
An open-source global energy system model developed by an international group of researchers enables large-scale collaboration by providing a tool that can analyze the world’s energy system or any subset of it. Designed for operational as well as combined generation, storage and transmission expansion studies, the PyPSA-Earth scheme provides customizable data extraction for electricity demand, generation and medium to high-voltage networks from open sources.
The model can support energy system transition, power system, technology evaluation, technology phase-out plan, supply diversification and electricity market simulations and studies. It uses Atlite free software, which converts weather data into energy systems data, to model renewable energies such as solar, wind and hydropower.
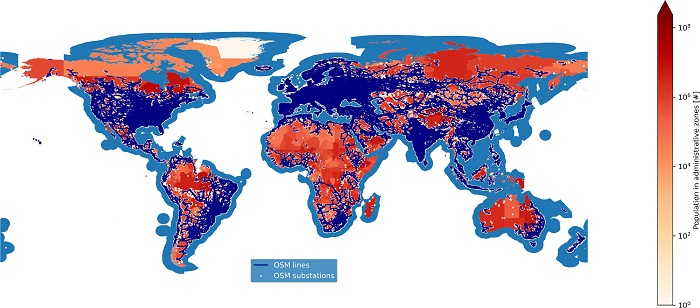 Representation of transmission networks by Open Street Map and shapes produced by PyPSA-Earth. Source: Appl Energy, 121096 (2023)
Representation of transmission networks by Open Street Map and shapes produced by PyPSA-Earth. Source: Appl Energy, 121096 (2023)
PyPSA-Earth was used to validate data for the African continent and for a 2060 net-zero planning study for Nigeria. The validation process outlined in Applied Energy confirmed that the new tool can generate power network and installed generation data that align with reliable national data, showcasing satisfactory accuracy. Multiple data sources and open-source tools to process raw data, such as OpenStreetMap, were integrated into the analysis to deliver realistic outcomes and higher spatial detail.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh (U.K.), Fraunhofer Research Institution for Energy Infrastructures and Geothermal Systems IEG (Germany), Justus-Liebig-University Giessen (Germany), Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (Germany), University of Pisa (Italy), Universität Berlin (Germany) and University of Applied Sciences (OTH) Regensburg (Germany) participated in this study.
