Helping to explain the abysmal results are excess inventory, weaker demand in China, challenging 5G comparisons, and elevated uncertainty.

Regional output deceleration was broad-based in the second quarter of 2024, reflecting slower revenue growth on a Y/Y basis in all regions, including North America, EMEA, Asia Pacific, and CALA (Caribbean and Latin America). Varied momentum in activity in the first half was particularly significant in China – the total telecom equipment market in China stumbled in the second quarter, declining 17% Y/Y.
The downward pressure was not confined to a specific technology, and initial readings show that all six telecom programs declined in the second quarter. In addition to the wireless programs (RAN and MCN), which are still impacted by slower 5G deployments, spending on SP Routers fell by a third in 2Q24.
Supplier rankings were mostly unchanged. The top 7 suppliers in 1H24 accounted for 80% of the worldwide telecom equipment market and included Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Cisco, Ciena, and Samsung. Huawei and ZTE combined gained nearly 3 percentage points of share between 2023 and 1H24.
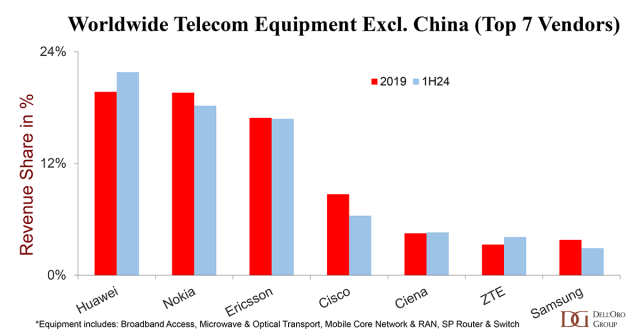
Supplier positions differ slightly if the Chinese market is excluded. Even with the ongoing efforts by the US government to curb Huawei’s rise, Huawei is still well positioned in the broader telecom equipment market, excluding China, which is up roughly two percentage points relative to 2019 levels.
Even with the second half expected to account for 54% of full-year revenues, market conditions are expected to remain challenging in 2024. The analyst team collectively forecasts global telecom equipment revenues to contract 8 to 10% in 2024, down from the 4% decline in 2023