It can detect nitrate (NO3, NO2) in water, and carbon dioxide (CO2) and Nitric Oxide (NO) in gas. Possible applications for the LED include chemical analysis, water quality monitoring and gas sensing.
The SF2-3T9B5L1-TB features UVC wavelengths down to 230nm (typical 233nm). And compared to the SF1, there is doubled output power and an improvement in temperature stability. A collimated ball lens provides its 17° effective beam angle. According to the Brisbane-based company, there is also a doubling of typical radiant intensity to 2 mw/Sr.
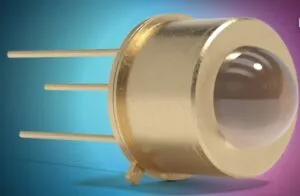
The unit is encapsulated in a standard (TO-39) compact Transistor Outline (TO-can) hermetically-sealed package.
Detection
Silanna writes:
“The SF2 is designed for precise detection and reliable disinfection in demanding environments, with the collimated ball lens providing a 17° effective beam angle. It is ideal for detection of nitrate (NO3) and nitrite (NO2) in water, and detection of carbon dioxide (CO2) and Nitric Oxide (NO) in gas. These features make this far UVC LED excellent for applications such as chemical and biological analysis, water quality monitoring, gas sensing, liquid chromatography, and disinfection.”
The company also highlights the LEDs contain no mercury, and are more robust than traditional UV lamps.
Silanna UV
Silanna UV will be showcasing the product at the 2025 IUVA World Congress, in Lisbon, and CIOE 2025, in Shenzhen.
Starting in 2006, the Silanna Group is an Australian semiconductor manufacturer established in 2006. It is privately funded since being acquired from Peregrine Semiconductor in 2008. Silanna UV has its headquarters in Brisbane and is an ISO 9001:2015 manufacturer.
UV-C defines ultraviolet radiation within a wave length range of 280 – 100 nanometres.
